Vendor Rating
Vendor rating, also known as supplier rating or supplier evaluation, is the process of assessing and evaluating the performance of a vendor or supplier based on specific criteria. The purpose of vendor rating is to ensure that the organization is working with the best possible suppliers who meet the organization’s quality, delivery, cost, and other requirements.
The vendor rating process typically involves the following steps:
Defining criteria: The organization should define the criteria for vendor rating, which may include quality, delivery, price, service, responsiveness, and reliability.
Collecting data: The organization should collect data on each vendor’s performance based on the defined criteria. The data can be collected through various sources, such as feedback from internal stakeholders, supplier self-assessments, and on-site audits.
Analyzing data: The organization should analyze the data to identify the strengths and weaknesses of each vendor’s performance. The analysis can be done through various tools, such as statistical analysis and benchmarking.
Rating vendors: The organization should rate each vendor’s performance based on the analysis of the data. The rating can be done through a numerical scale or a qualitative rating, such as excellent, good, satisfactory, or unsatisfactory.
Taking action: Based on the vendor ratings, the organization should take appropriate action, such as renegotiating contracts, working with suppliers to improve performance, or terminating relationships with underperforming vendors.
The benefits of vendor rating include improved supplier performance, reduced risk, increased cost savings, and better quality of products and services. By regularly assessing and evaluating vendors, organizations can ensure that they are working with the best possible suppliers who meet their specific requirements and contribute to their overall success.
Vendor Selection
Vendor selection is the process of choosing a vendor or supplier to provide goods or services to an organization. The vendor selection process typically involves the following steps:
Identify potential vendors: The organization should identify potential vendors who can meet its specific requirements. This can be done through various sources, such as referrals, online searches, and trade shows.
Evaluate vendor capabilities: The organization should evaluate the capabilities of each vendor, such as their capacity, expertise, quality standards, and financial stability. This can be done through a request for information (RFI) or a request for proposal (RFP).
Shortlist vendors: Based on the evaluation, the organization should shortlist vendors who meet its specific requirements and are capable of providing the required goods or services.
Request for quotation: The organization should request quotations from the shortlisted vendors, which should include the price, delivery schedule, and other terms and conditions.
Evaluate quotations: The organization should evaluate the quotations received from the shortlisted vendors based on the price, delivery schedule, quality, and other factors.
Negotiate terms and conditions: The organization should negotiate the terms and conditions of the contract with the selected vendor, such as price, delivery schedule, quality standards, warranties, and payment terms.
Award contract: The organization should award the contract to the selected vendor who meets its specific requirements and has agreed to the negotiated terms and conditions.
Monitor vendor performance: The organization should monitor the performance of the selected vendor to ensure that they meet the required standards and deliver the goods or services as per the agreed schedule.
The vendor selection process is critical to the success of an organization, as it ensures that it works with the best possible vendors who meet its specific requirements and contribute to its overall success. By following a structured vendor selection process, organizations can minimize the risk of working with underperforming vendors and maximize the benefits of working with the best possible suppliers.
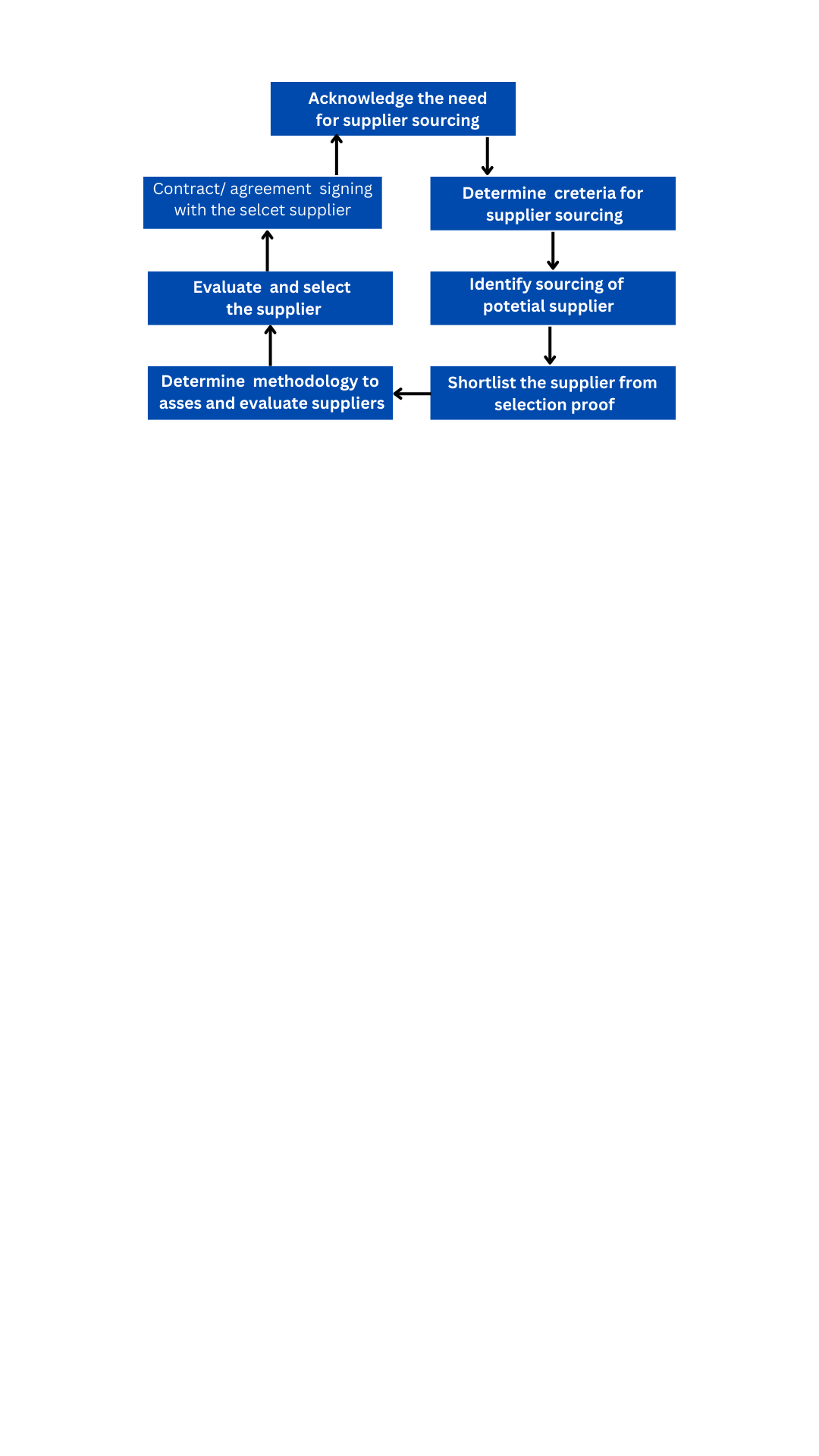
Vendor rating process
The vendor rating process involves evaluating and rating a supplier’s performance based on several criteria, including quality, delivery performance, cost, responsiveness, and communication. The process typically involves the following steps:
Identify the criteria: The first step is to identify the criteria that will be used to evaluate the supplier’s performance. This may include factors such as quality, delivery performance, cost, responsiveness, communication, and innovation.
Collect data: The organization should collect data on the supplier’s performance using various methods such as surveys, site visits, and audits. The data collected should be objective and relevant to the criteria identified in step one.
Evaluate performance: The organization should evaluate the supplier’s performance based on the data collected. This may involve assigning a rating or score to each criterion and calculating an overall rating for the supplier.
Communicate results: The organization should communicate the results of the evaluation to the supplier. This may include providing feedback on areas where the supplier performed well and areas for improvement.
Take action: The organization should take action based on the results of the evaluation. If the supplier has performed well, the organization may continue to work with the supplier and provide them with additional business opportunities. If the supplier has not performed well, the organization may work with the supplier to improve their performance or consider finding an alternative supplier.
Monitor performance: The organization should continue to monitor the supplier’s performance over time to ensure that they continue to meet the organization’s requirements. This may involve setting up regular performance reviews and tracking the supplier’s performance against the criteria identified in step one.
The vendor rating process should be conducted regularly and should be based on a clear set of criteria. The process should be objective and transparent, and should ensure that the selected suppliers meet the organization’s requirements in terms of quality, cost, delivery, and risk.
Factor affecting selection of optimal supplier and vendor ratings
There are several factors that can affect the selection of an optimal supplier and the vendor rating, including:
Quality: The quality of the supplier’s products or services is a critical factor in selecting an optimal supplier. Organizations should evaluate the quality of the supplier’s products or services to ensure that they meet the organization’s standards.
Cost: Cost is another important factor in selecting an optimal supplier. Organizations should consider the supplier’s pricing and determine whether it is reasonable and competitive.
Delivery performance: Delivery performance is another critical factor in selecting an optimal supplier. Organizations should evaluate the supplier’s ability to deliver products or services on time and in the required quantity.
Financial stability: The financial stability of the supplier is an important factor to consider. Organizations should evaluate the supplier’s financial stability to ensure that they can meet their financial obligations and continue to provide products or services over the long term.
Responsiveness: Responsiveness is another important factor to consider when selecting a supplier. Organizations should evaluate the supplier’s ability to respond to requests for information or support in a timely and effective manner.
Communication: Effective communication between the organization and the supplier is essential. Organizations should evaluate the supplier’s communication skills and determine whether they can communicate effectively with the organization.
Innovation: Innovation is becoming increasingly important in today’s fast-paced business environment. Organizations should evaluate the supplier’s ability to innovate and introduce new products or services that can help the organization stay competitive.
Risk management: Organizations should evaluate the supplier’s risk management practices to ensure that they can effectively manage potential risks such as supply chain disruptions, quality issues, and financial instability.
Cultural fit: Cultural fit is an important factor in supplier selection. Organizations should consider the supplier’s values, culture, and approach to business to ensure that they align with the organization’s values and culture.
By considering these factors, organizations can select an optimal supplier and accurately rate their vendors, ensuring that they meet the organization’s requirements in terms of quality, cost, delivery, and risk.
Suppliers Evaluation methods/ Vendor ratings method
There are several methods that organizations can use to evaluate suppliers and rate their vendors. Some of these methods include:
Performance Scorecards: This method involves the use of a scorecard that rates suppliers based on various performance metrics such as delivery performance, quality, responsiveness, and cost. This method is often used to track the supplier’s performance over time and identify areas for improvement.
Supplier Audits: This method involves conducting an audit of the supplier’s facilities and processes to assess their compliance with regulatory and quality requirements. This method is often used to evaluate the supplier’s overall quality management system and identify areas for improvement.
Surveys: This method involves sending surveys to the supplier’s customers to gather feedback on their performance. This method is often used to evaluate the supplier’s communication skills, responsiveness, and overall customer satisfaction.
Site Visits: This method involves visiting the supplier’s facilities to assess their production capabilities, quality control processes, and overall operations. This method is often used to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing processes and identify areas for improvement.
Collaborative Performance Reviews: This method involves working collaboratively with the supplier to identify areas for improvement and develop action plans to address them. This method is often used to build a strong relationship with the supplier and improve their overall performance.
Financial Analysis: This method involves analyzing the supplier’s financial statements to assess their financial stability and risk of default. This method is often used to evaluate the supplier’s financial health and identify potential risks.
Organizations may use one or more of these methods to evaluate their suppliers and rate their vendors. The method chosen will depend on the organization’s specific requirements and the supplier’s industry, size, and complexity.
Financial Analysis: This method involves analyzing the supplier’s financial statements to assess their financial stability and risk of default. This method is often used to evaluate the supplier’s financial health and identify potential risks.
Organizations may use one or more of these methods to evaluate their suppliers and rate their vendors. The method chosen will depend on the organization’s specific requirements and the supplier’s industry, size, and complexity.
Advantage of vendor /supplier Ratings
There are several advantages of vendor/supplier ratings for organizations, including:
Improved supplier performance: Vendor/supplier ratings provide organizations with a framework for evaluating supplier performance and identifying areas for improvement. This allows organizations to work with their suppliers to address performance issues and improve overall supplier performance.
Better decision-making: Vendor/supplier ratings provide organizations with objective data to support their decision-making processes. This allows organizations to make informed decisions about which suppliers to work with and how to allocate resources to different suppliers.
Cost savings: Vendor/supplier ratings can help organizations identify opportunities to reduce costs by working with more efficient and effective suppliers. This can lead to significant cost savings over time.
Risk mitigation: Vendor/supplier ratings can help organizations identify potential risks associated with their suppliers, such as quality issues, delivery delays, and financial instability. This allows organizations to take proactive measures to mitigate these risks and ensure continuity of supply.
Improved relationships: Vendor/supplier ratings can help organizations build stronger relationships with their suppliers by providing a clear framework for communication, performance evaluation, and feedback. This can lead to improved collaboration, better communication, and increased trust between the organization and its suppliers.
Overall, vendor/supplier ratings can provide significant benefits for organizations by improving supplier performance, supporting better decision-making, reducing costs, mitigating risks, and building stronger relationships with suppliers.
Identify and evaluating the international supplier
Identifying and evaluating international suppliers can be a complex process. Here are some steps that organizations can follow:
Identify potential suppliers: Organizations can use various sources to identify potential international suppliers, including trade shows, industry publications, online directories, and referrals from other businesses. Organizations can also reach out to trade associations, embassies, and trade commissions for recommendations.
Conduct initial screening: Once potential suppliers have been identified, organizations should conduct an initial screening to evaluate their suitability. This screening may include evaluating the supplier’s product quality, production capabilities, financial stability, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Conduct a background check: Organizations should conduct a background check on the supplier to verify their legitimacy and reputation. This may involve conducting a credit check, reviewing legal records, and checking references.
Conduct a site visit: Organizations should consider conducting a site visit to the supplier’s facilities to assess their production capabilities, quality control processes, and overall operations. This can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s ability to meet the organization’s needs.
Request samples: Organizations should request samples of the supplier’s products to evaluate their quality and ensure that they meet the organization’s requirements.
Request quotes: Organizations should request quotes from potential suppliers to compare pricing and determine the most cost-effective option.
Evaluate supplier performance: Once a supplier has been selected, organizations should continue to monitor their performance to ensure that they are meeting expectations. This may involve conducting periodic performance reviews and using a vendor/supplier rating system.
When evaluating international suppliers, organizations should also consider factors such as language and cultural differences, currency exchange rates, shipping and logistics, and import/export regulations. It is important to carefully evaluate potential suppliers to ensure that they are a good fit for the organization’s needs and can provide reliable and high-quality products or services.