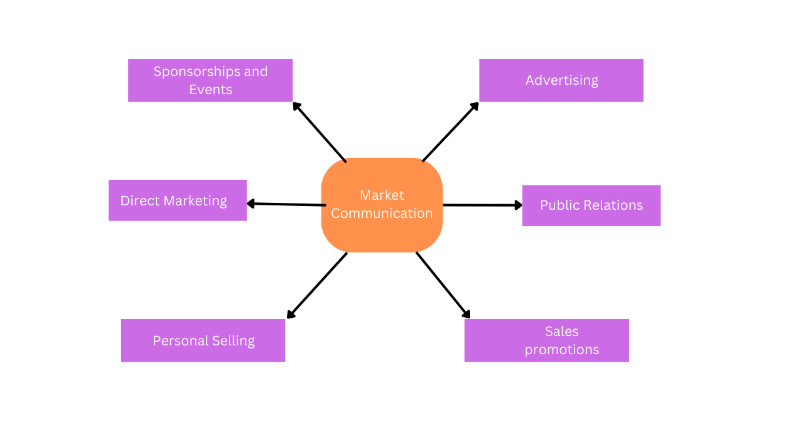
Market Communication
Market communication, also known as marketing communication or marcom, refers to the use of various channels and tools to communicate a company’s message to its target audience. The goal of market communication is to create awareness, interest, and demand for a product or service.
Here are some common elements of market communication:
Advertising: This refers to paid communication that promotes a product or service through various media channels, such as television, radio, print, online, and outdoor advertising.
Public Relations: This involves building relationships with media outlets, influencers, and other stakeholders to generate positive publicity and manage a company’s reputation.
Sales Promotion: This refers to short-term incentives, such as discounts, coupons, or free samples, that encourage customers to purchase a product or service.
Personal Selling: This involves direct communication between a salesperson and a potential customer to promote a product or service and close a sale
Direct Marketing: This involves reaching out to potential customers directly through channels such as email, direct mail, or telemarketing.
Sponsorships and Events: This involves sponsoring events or creating brand experiences to build awareness and engagement with target audiences.
Effective market communication requires a clear understanding of the target audience, their needs and preferences, and the channels and messaging that will resonate with them. It also requires a coordinated approach across different communication channels and a focus on measuring and optimizing results to improve the return on investment.
Brand expression
Brand expression refers to the various ways that a brand communicates its identity, values, and personality to its target audience. It includes all the visual and verbal elements that contribute to the brand’s overall image and perception in the minds of consumers. Here are some key elements of brand expression:
Brand Identity: This includes the brand name, logo, tagline, and other visual and verbal elements that help to differentiate the brand from its competitors.
Brand Messaging: This includes the brand’s tone of voice, messaging platform, key messages, and brand story. These elements help to communicate the brand’s values, purpose, and unique selling proposition to its target audience.
Visual Branding: This includes the use of color, typography, imagery, and other design elements to create a visual identity for the brand. This can include the design of the brand’s packaging, website, advertising, and other marketing materials.
Brand Experience: This includes all the touchpoints that a customer has with the brand, including product design, customer service, retail environment, and other interactions. A positive brand experience can help to build brand loyalty and advocacy among customers.
Brand Guidelines: These are the rules and guidelines that govern the use of the brand’s visual and verbal elements. This helps to ensure consistency and clarity in how the brand is presented across different channels and touchpoints.
Effective brand expression requires a deep understanding of the target audience and the competitive landscape, as well as a strong sense of the brand’s identity, values, and personality. It also requires careful planning and execution across all the elements of brand expression to ensure a consistent and compelling brand image.
Managing and Administering channel members
Managing and administering channel members involves developing and maintaining effective relationships with intermediaries such as wholesalers, distributors, and retailers. Effective management of channel members is critical to ensuring that the company’s products or services reach the end consumer in a timely and cost-effective manner.
The following are some key steps involved in managing and administering channel members:
Training and support: Providing training and support to channel members is critical to ensuring that they have the necessary knowledge and skills to effectively promote and sell the company’s products or services. This may involve providing product training, sales training, and ongoing support to help channel members achieve their goals.
Performance monitoring: Monitoring the performance of channel members is critical to identifying areas where improvements can be made. This may involve tracking sales figures, customer feedback, and other key performance indicators to help identify opportunities for improvement.
Incentives and rewards: Providing incentives and rewards to channel members can be an effective way to motivate them to perform at a high level. This may include offering discounts or bonuses for meeting sales targets, or providing other incentives such as training opportunities or exclusive access to new products.
Communication: Maintaining open and effective communication with channel members is critical to building strong relationships. This may involve regular meetings, email updates, and other forms of communication to keep channel members informed about product updates, promotions, and other important information.
Conflict resolution: Finally, managing and administering channel members may involve resolving conflicts that arise between different intermediaries. This may involve mediation, negotiation, or other strategies to help resolve disputes and maintain positive relationships between all parties involved.
Overall, effective management and administration of channel members is critical to ensuring that a company’s products or services reach their intended market in a timely and cost-effective manner. By providing training and support, monitoring performance, providing incentives and rewards, maintaining open communication, and resolving conflicts, companies can build strong relationships with their channel members and achieve their business goals.
Direct and Indirect channels
Direct and indirect channels are two different methods of distributing products or services to customers.
Direct channels involve selling products or services directly to customers without the involvement of intermediaries. For example, a company may sell its products directly to consumers through its own website or retail stores.
Indirect channels, on the other hand, involve the use of intermediaries such as wholesalers, distributors, or retailers to sell products or services to customers. For example, a company may sell its products to a distributor who then sells the products to retailers, who in turn sell the products to consumers.
There are advantages and disadvantages to both direct and indirect channels. Direct channels allow companies to have more control over the sales process and to build a direct relationship with customers, which can be valuable for building brand loyalty and obtaining customer feedback. However, direct channels can be more expensive to set up and maintain, and may require significant investments in marketing and sales resources.
Indirect channels, on the other hand, can be more cost-effective and may allow companies to reach a wider audience by leveraging the expertise and resources of intermediaries. However, indirect channels may also result in reduced control over the sales process and may limit the company’s ability to build direct relationships with customers.
Ultimately, the choice between direct and indirect channels will depend on a variety of factors, including the company’s resources, target market, and business goals. Many companies use a combination of both direct and indirect channels to maximize their reach and effectiveness.
Supply chain and logistics management
Supply chain and logistics management are two related but distinct concepts that are essential to the effective management and operation of businesses that rely on the movement of goods or materials.
Supply chain management refers to the coordination of activities involved in the production and delivery of products or services to customers. This can include sourcing materials and components, managing suppliers, overseeing production processes, managing inventory, and coordinating transportation and logistics.
Logistics management, on the other hand, specifically focuses on the movement and storage of goods within the supply chain. This includes managing the transportation and storage of materials and products, as well as the coordination of related activities such as order processing and inventory management.
Effective supply chain and logistics management requires careful planning, coordination, and execution of a variety of activities, including:
Sourcing and procurement: This involves identifying and selecting suppliers, negotiating contracts, and managing relationships with suppliers.
Production and operations management: This involves managing the production process, including planning production schedules, managing inventory levels, and ensuring quality control.
Transportation and distribution management: This involves managing the movement of goods between different locations, including the selection of transportation modes, the management of transportation providers, and the tracking and monitoring of shipments.
Inventory management: This involves managing inventory levels and ensuring that products are available when and where they are needed.
Customer service management: This involves managing customer orders, responding to customer inquiries and complaints, and ensuring that customer needs are met.
Effective supply chain and logistics management can help businesses to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction, ultimately leading to increased profitability and competitiveness.