Pricing and Negotiations
Pricing and negotiations are two important aspects of sales and marketing that can have a significant impact on the success of a business.
Pricing refers to the process of determining the price at which a product or service will be sold to customers. This involves considering factors such as the cost of production, competitive pricing, and customer demand, as well as factors such as the company’s brand image and target market. Setting the right price is crucial for maximizing profitability while also ensuring that the product or service remains competitive in the marketplace.
Price models and skills, Price tactics, Negotiated pricings
There are several pricing models and tactics that businesses can use to effectively set prices and negotiate pricing with customers. Some of these include:
Cost-plus pricing: This involves calculating the cost of producing a product or service and then adding a markup to determine the selling price.
Value-based pricing: This involves setting prices based on the perceived value of the product or service to the customer, rather than the cost of production.
Competitive pricing: This involves setting prices based on the prices of competitors in the same market.
Dynamic pricing: This involves setting prices based on real-time demand, such as offering discounts during slow periods or increasing prices during peak demand.
In addition to these pricing models, there are several pricing tactics that businesses can use to negotiate pricing with customers, including:
Price bundling: Offering discounts for purchasing multiple products or services together.
Price skimming: Setting high prices initially and then gradually lowering them over time.
Psychological pricing: Setting prices that end in certain numbers (e.g. $9.99 instead of $10) to create the perception of a lower price.
Promotional pricing: Offering temporary discounts or special offers to drive sales.
Negotiated pricing involves the process of reaching an agreement between a business and its customers or suppliers on a specific price or pricing structure. This may involve negotiating discounts, volume discounts, or other terms that are mutually beneficial for both parties. Effective negotiation skills are essential for businesses to ensure that they are able to reach favorable pricing agreements that support their financial goals and objectives. Some key negotiation skills include active listening, problem-solving, and the ability to communicate persuasively and effectively.
Pricing settings in B2B markets
Setting prices in B2B markets can be more complex than in consumer markets due to the nature of the customer base, the complexity of the products or services offered, and the long-term relationships that exist between businesses. Here are some pricing settings that are commonly used in B2B markets:
Negotiated pricing: This involves negotiating pricing with each customer on an individual basis, taking into account factors such as the customer’s volume, payment terms, and delivery requirements.
Volume pricing: This involves offering discounts to customers who purchase large quantities of products or services.
Cost-plus pricing: This involves calculating the cost of producing a product or service and then adding a markup to determine the selling price.
Value-based pricing: This involves setting prices based on the perceived value of the product or service to the customer, rather than the cost of production.
Dynamic pricing: This involves setting prices based on real-time demand, such as offering discounts during slow periods or increasing prices during peak demand.
In B2B markets, it is important to consider the total cost of ownership (TCO) for the customer, which includes not just the purchase price but also the cost of implementing, using, and maintaining the product or service over its lifetime. This means that pricing strategies should take into account factors such as after-sales service and support, warranties, and training to ensure that customers are getting the best value for their investment. Additionally, it is important to ensure that pricing is consistent across different channels and regions to maintain transparency and fairness for all customers.
3c’s of Pricing cost , Customer and competition pricing startegies
The 3C’s of pricing are cost, customer, and competition. Here’s how each of these factors can inform pricing strategies:
Cost: This refers to the cost of producing and delivering the product or service. Cost-based pricing strategies involve adding a markup to the cost of production to determine the selling price. This can include strategies such as cost-plus pricing or target return pricing.
Customer: This refers to the value that the product or service provides to the customer. Value-based pricing strategies involve setting prices based on the perceived value of the product or service to the customer, rather than the cost of production. This can include strategies such as skimming pricing or penetration pricing.
Competition: This refers to the pricing strategies of other businesses in the market. Competitive pricing strategies involve setting prices based on the prices of similar products or services offered by competitors. This can include strategies such as price matching or undercutting competitors’ prices.
Effective pricing strategies often involve a combination of these factors. For example, a business may use cost-based pricing to ensure that they are covering their costs, but also take into account the value that the product or service provides to customers to set a competitive price. Similarly, a business may use value-based pricing to set a premium price for a high-quality product or service, but also consider the prices of competitors to ensure that the price is reasonable in the market. By considering the 3C’s of pricing, businesses can develop pricing strategies that are effective at maximizing profitability while also meeting the needs and expectations of customers and staying competitive in the market.
Price positioning
Price positioning is the process of determining where a product or service falls in relation to other products or services in terms of price. This involves identifying the target market and competitors, and then developing a pricing strategy that positions the product or service in a way that is attractive to the target market and differentiates it from competitors.
Price positioning can involve setting prices higher or lower than competitors depending on the target market’s perceived value of the product or service. For example, a business may position their product as a high-end luxury item with a premium price to appeal to customers who value luxury and are willing to pay more for it. Alternatively, a business may position their product as a budget-friendly option with a lower price to appeal to customers who are price-sensitive and looking for a bargain.
When positioning a product or service based on price, it is important to consider the overall value proposition and ensure that the price aligns with the perceived value of the product or service. This can involve considering factors such as quality, features, and benefits in addition to price. By effectively positioning the product or service based on price, businesses can attract and retain customers, increase profitability, and differentiate themselves from competitors in the market.
Roles of Sales forces in pricing
Sales forces play a critical role in pricing for B2B organizations. Their role includes:
Gathering information: Salespeople are in direct contact with customers, and they are in the best position to gather information about the customers’ needs, preferences, and price sensitivity. They can provide valuable feedback to the pricing team and help them make informed decisions about pricing.
Communicating pricing strategy: Salespeople need to be informed about the company’s pricing strategy and the rationale behind it. This helps them to communicate the value proposition effectively to customers and make a convincing case for the pricing.
Negotiating prices: Salespeople are often responsible for negotiating prices with customers. They need to have the skills to negotiate effectively while still maintaining a profitable price point for the company.
Building relationships: Salespeople are the face of the company, and they play a crucial role in building and maintaining relationships with customers. Pricing can be an important part of this relationship-building process, as it demonstrates the company’s commitment to providing value to the customer.
Monitoring pricing performance: Salespeople need to monitor the impact of pricing on sales performance and customer satisfaction. They can provide feedback on the effectiveness of pricing strategies and help the pricing team to make adjustments as needed.
Overall, the sales force plays a critical role in the pricing process, and effective collaboration between the pricing and sales teams is essential for success in B2B markets.
Bid Pricing
Bid pricing is a pricing strategy used by B2B companies in response to a customer’s request for proposal (RFP) or bid. In bid pricing, the company submits a proposal or bid that outlines the products or services they will provide, along with the associated pricing.
Bid pricing can be a complex process, as companies need to take into account a range of factors, such as:
Cost of goods sold: Companies need to calculate their costs of production, including materials, labor, and overhead, to determine the minimum price they can offer.
Competitive landscape: Companies need to consider the pricing strategies of their competitors and the prevailing market rates for similar products or services.
Profit margin: Companies need to set a profit margin that allows them to cover their costs and generate a reasonable return on investment.
Customer value: Companies need to consider the value that their products or services will bring to the customer, and price accordingly.
In bid pricing, companies need to balance the need to win the contract with the need to maintain profitability. If the bid is too high, the company may lose the contract to a competitor, while if the bid is too low, the company may not make a profit.
Effective bid pricing requires careful analysis of the cost of production, the competitive landscape, and the customer’s needs and preferences. It also requires effective communication and collaboration between the pricing and sales teams to ensure that the bid reflects the company’s overall pricing strategy and value proposition.
Internet Auctions
Internet auctions are online marketplaces where buyers and sellers come together to exchange goods or services through an auction-style process. In internet auctions, the seller offers a product or service for sale, and potential buyers bid on the item until the auction closes.
Internet auctions have become popular in recent years due to their convenience and accessibility. They provide a platform for buyers and sellers from all over the world to participate in an auction from the comfort of their homes or offices. Internet auctions can be used to sell a wide range of products, including consumer goods, industrial equipment, and even real estate.
There are different types of internet auctions, including:
English auctions: This is the most common type of internet auction, where the seller sets a minimum bid price, and buyers bid higher until the auction ends.
Dutch auctions: In this type of auction, the seller offers multiple items for sale at a fixed price. Buyers can purchase one or more items at the fixed price until all items are sold.
Reverse auctions: In this type of auction, the buyer sets the maximum price they are willing to pay, and sellers bid lower until the auction closes.
Internet auctions have several advantages for both buyers and sellers. For buyers, internet auctions provide access to a wide range of products and the opportunity to purchase items at a lower price. For sellers, internet auctions provide a global market for their products and the opportunity to sell items quickly.
However, internet auctions also have some drawbacks, such as the risk of fraud, the difficulty of verifying the quality of products, and the potential for bidding wars that drive prices higher than the item’s value.
Ethical aspects of B2B pricing
Ethical aspects of B2B pricing involve considerations of fairness, honesty, and transparency in pricing practices. It is important for businesses to consider ethical principles when pricing their products or services to maintain trust and credibility with their customers.
Some ethical considerations in B2B pricing include:
Price discrimination: Price discrimination occurs when a company charges different prices to different customers for the same product or service. While price discrimination is legal in some cases, it can be unethical if it unfairly disadvantages certain customers.
Predatory pricing: Predatory pricing occurs when a company sets prices below cost to drive competitors out of the market. This can be considered unethical because it harms other businesses and can lead to reduced competition and higher prices in the long term.
Hidden fees: Hidden fees are charges that are not disclosed upfront and can be considered unethical if they mislead customers or make it difficult for them to compare prices.
Price fixing: Price fixing is when companies collude to set prices at a certain level, which can be considered illegal and unethical.
Transparency: Transparency in pricing involves providing customers with clear information about the price of a product or service, including any additional fees or charges. This is important for building trust and maintaining good relationships with customers.
Businesses should also consider ethical aspects of pricing in relation to their impact on society and the environment. For example, setting prices that take into account the true cost of production, including environmental and social costs, can be seen as ethical and socially responsible.
Managing the personal selling function
Managing the personal selling function involves overseeing the sales team’s activities to achieve the organization’s sales objectives. Here are some key steps to manage the personal selling function effectively:
Define sales objectives: The first step in managing the personal selling function is to define the sales objectives. The sales objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. These objectives should align with the organization’s overall business goals and marketing plan.
Build a strong sales team: Hire and train a strong sales team that can represent the company well and sell the product or service effectively. Develop a sales training program that includes product knowledge, sales skills, and customer service skills.
Develop a sales plan: Develop a sales plan that outlines the sales team’s responsibilities, target market, sales strategies, and tactics. The sales plan should align with the organization’s overall business goals and marketing plan.
Monitor sales performance: Monitor the sales team’s performance regularly to ensure that they are meeting their sales objectives. Analyze the sales data to identify areas where the sales team can improve their performance.
Provide feedback and coaching: Provide regular feedback and coaching to the sales team to help them improve their performance. Use data-driven insights to identify areas where they can improve their sales skills and provide targeted training to address those areas.
Use technology to improve efficiency: Use technology to improve the efficiency of the sales process. Use customer relationship management (CRM) software to track customer interactions and sales data. Use sales analytics tools to gain insights into the sales process and identify areas for improvement.
Align the sales function with marketing and other departments: Ensure that the sales function is aligned with other departments, especially marketing. Marketing and sales should work together to develop effective sales strategies that support the organization’s overall business goals.
Sales forces selections
Sales force selection refers to the process of identifying, recruiting, and hiring individuals who are best suited to work in a sales role. The goal of sales force selection is to build a team of salespeople who have the right skills, experience, and personality traits to sell a company’s products or services effectively.
Here are some key steps involved in sales force selection:
Define the sales job requirements: Start by defining the sales job requirements. This involves identifying the key skills, experience, and personality traits that are needed for success in the role. This information can be gathered through job analysis and interviews with current successful salespeople.
Develop a candidate pool: Next, develop a candidate pool by advertising the position on job boards, social media, and other relevant platforms. You can also reach out to recruiting firms to help identify potential candidates.
Screen candidates: Once you have a candidate pool, you can screen candidates by reviewing their resumes and cover letters, conducting initial phone or video interviews, and administering pre-employment assessments.
Conduct in-person interviews: After screening candidates, invite the most promising candidates for in-person interviews. During these interviews, you can assess their sales skills, experience, and personality traits.
Check references: Before making a job offer, check the candidate’s references to ensure that their past work experience aligns with what they have represented during the interview process.
Make a job offer: Once you have identified the best candidate, make a job offer that includes the job responsibilities, compensation package, and start date.
Overall, selecting the right sales force is critical to the success of any organization’s sales efforts. By following these key steps, you can build a high-performing sales team that can drive revenue growth and build lasting customer relationships.
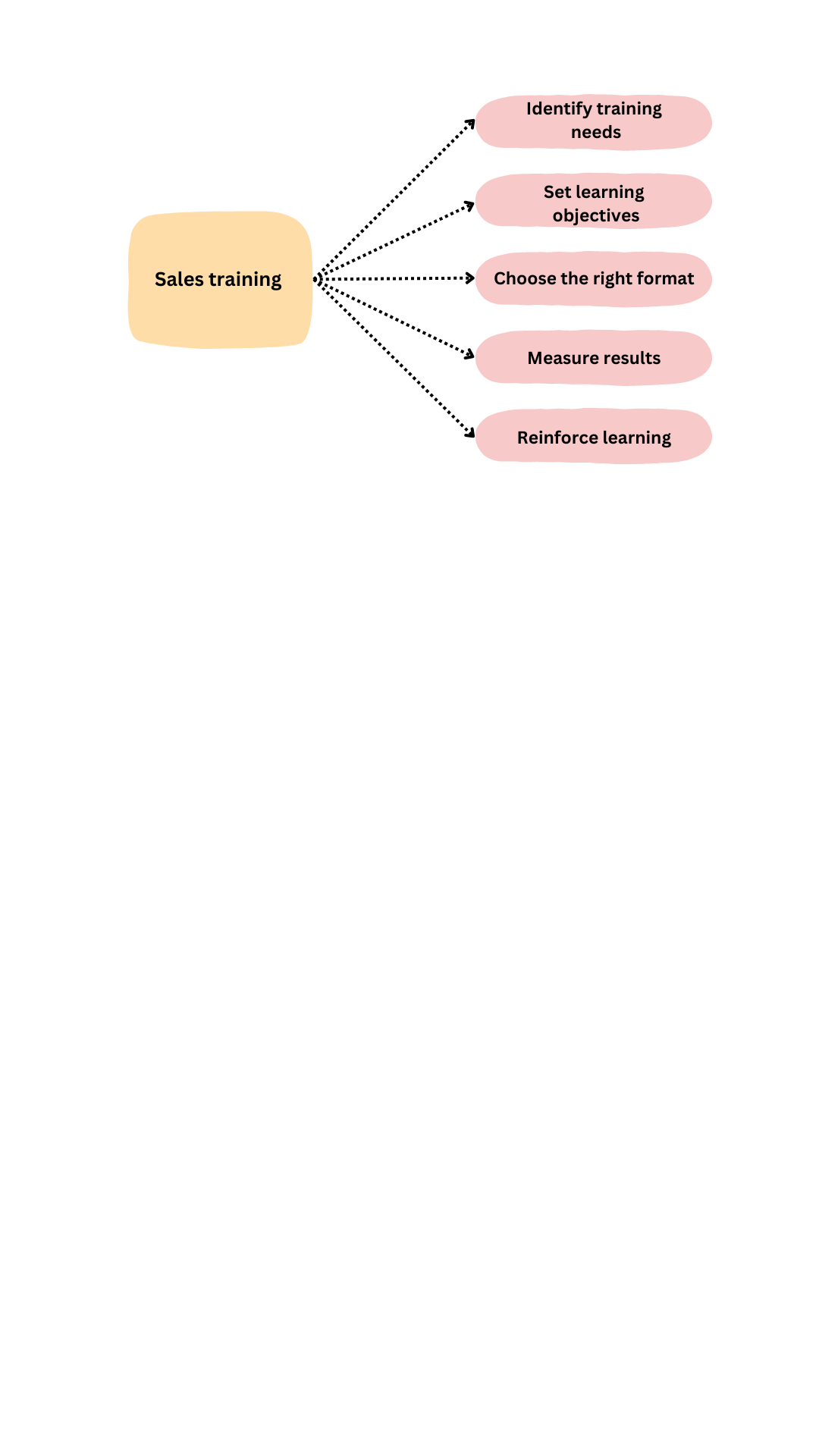
Sales training
Sales training is an essential component of developing a successful sales force. It helps salespeople develop the skills and knowledge needed to sell effectively and build strong relationships with customers. Here are some key steps to consider when developing and implementing a sales training program:
Identify training needs: Begin by identifying the specific skills and knowledge gaps that exist among your sales team. You can do this by conducting a needs assessment that involves analyzing sales data, surveying customers, and soliciting feedback from sales team members and managers.
Set learning objectives: Based on the needs assessment, set specific learning objectives for the sales training program. These objectives should be focused on the specific skills and knowledge areas that need to be developed.
Choose the right format: Decide on the format of the sales training program. This can be in-person, virtual, or a combination of both. Consider factors such as the size and location of your sales team, budget constraints, and the nature of the content being covered.
Measure results: Measure the effectiveness of the sales training program by gathering feedback from the sales team and evaluating the impact on sales performance. Use this feedback to refine and improve the training program over time.
Reinforce learning: Reinforce the learning by providing ongoing support and coaching to your sales team. This can include regular check-ins, performance reviews, and additional training sessions as needed.
Overall, sales training is a critical component of building a successful sales force. By identifying training needs, setting learning objectives, choosing the right format, developing training materials, delivering the training, measuring results, and reinforcing learning, you can help your sales team develop the skills and knowledge needed to succeed.
Sales control and Evaluations
Sales control refers to the process of monitoring and managing the sales activities of a company to ensure they align with the overall business objectives. It involves setting sales targets, measuring performance, identifying areas of improvement, and taking corrective actions.
Sales evaluations, on the other hand, refer to the process of assessing the effectiveness of a company’s sales strategies and tactics. This can be done through various methods such as analyzing sales data, conducting customer surveys, and comparing sales performance with industry benchmarks.
Overall, sales control and evaluations are essential for companies to optimize their sales performance and achieve their business goals.