Human Resources planning
Human resources planning is a process of forecasting an organization’s future human resource needs and developing strategies to meet those needs.
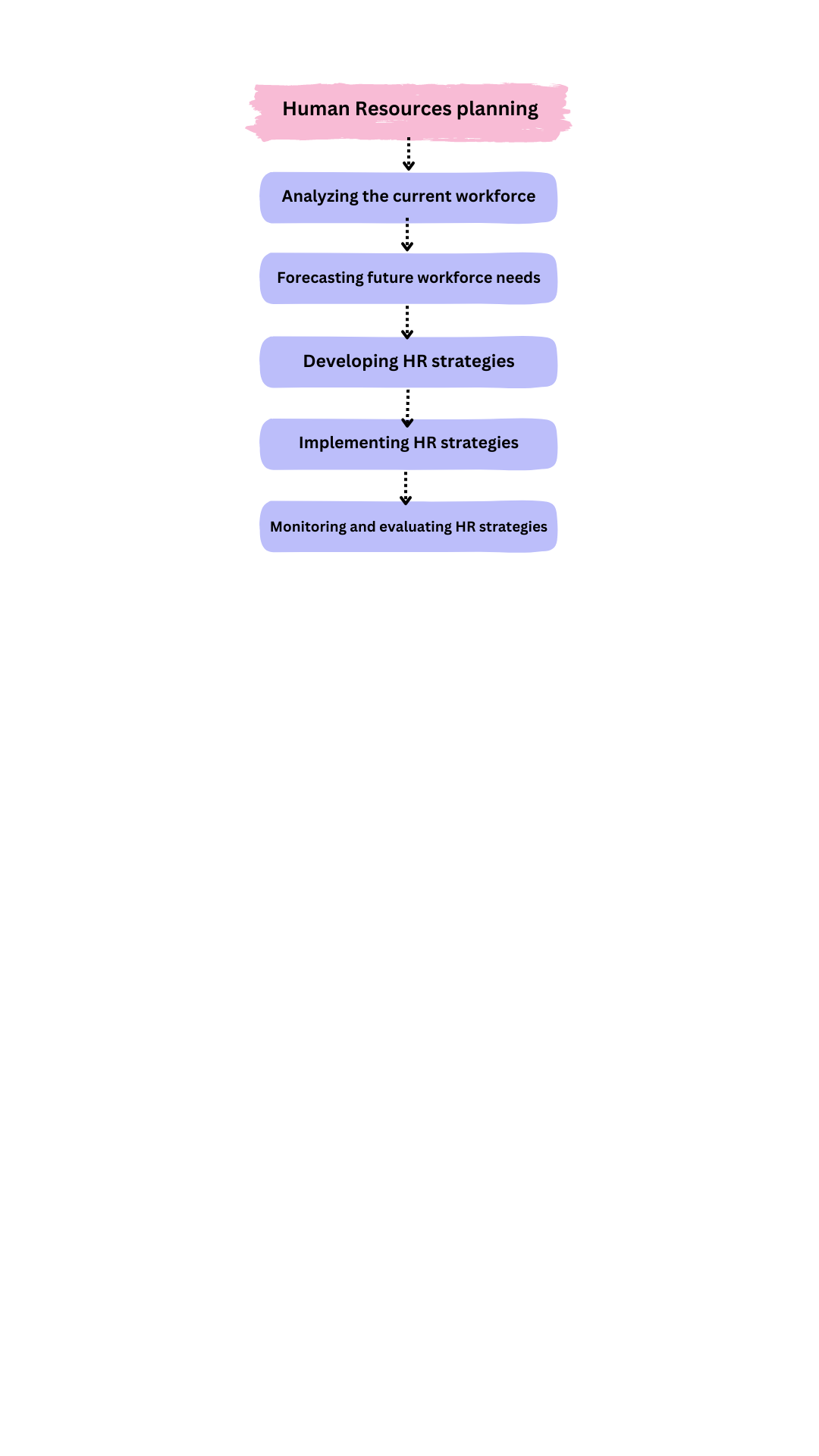
It involves analyzing the current workforce, assessing future workforce needs, and implementing HR strategies to address any gaps. The process typically includes the following steps:
Analyzing the current workforce: This involves assessing the organization’s current workforce in terms of skills, competencies, demographics, and other factors. This analysis provides a baseline for future workforce planning.
Forecasting future workforce needs: This involves projecting future workforce needs based on factors such as growth, turnover, retirement, and changes in business strategy. This analysis helps to identify potential gaps in the workforce and anticipate future talent requirements.
Developing HR strategies: Based on the analysis of the current and future workforce, HR strategies can be developed to address any gaps. These may include recruitment, training and development, succession planning, retention strategies, and workforce restructuring.
Implementing HR strategies: The HR strategies are then implemented, which may involve hiring new employees, offering training and development programs, promoting internal talent, or restructuring the workforce.
Monitoring and evaluating HR strategies: Once the HR strategies are implemented, they need to be monitored and evaluated to ensure they are meeting the organization’s goals and objectives. This includes measuring the effectiveness of recruitment and retention efforts, tracking employee performance, and assessing the impact of training and development programs.
Effective human resources planning can help organizations to optimize their workforce, reduce labor costs, and increase productivity. It can also ensure that the organization has the right talent in place to meet its strategic goals and objectives.
Quantitative and Qualitative dimensions of HR planning
Quantitative and qualitative dimensions are two main aspects of human resources planning that help organizations to achieve their strategic goals and objectives.
Quantitative Dimensions:
The quantitative dimension of HR planning is focused on the numerical or measurable aspects of the workforce. It involves analyzing data related to workforce size, demographics, skills, competencies, turnover rates, and other metrics. This information can be used to make informed decisions about recruitment, training, and other HR strategies.
Examples of quantitative HR planning activities include forecasting future workforce needs, analyzing labor supply and demand, setting recruitment targets, and developing compensation and benefits packages based on market trends. The key benefit of quantitative HR planning is that it provides objective data and helps to ensure that HR decisions are aligned with business objectives.
Qualitative Dimensions:
The qualitative dimension of HR planning focuses on the subjective or non-measurable aspects of the workforce. It involves analyzing factors such as employee attitudes, values, and organizational culture. Qualitative data is often collected through surveys, interviews, focus groups, and other forms of employee feedback.