Exchange Risk: Exchange exposure and Exchange risk
Exchange risk, also known as currency risk or foreign exchange risk, is the risk of financial loss resulting from fluctuations in exchange rates. There are two key concepts related to exchange risk:
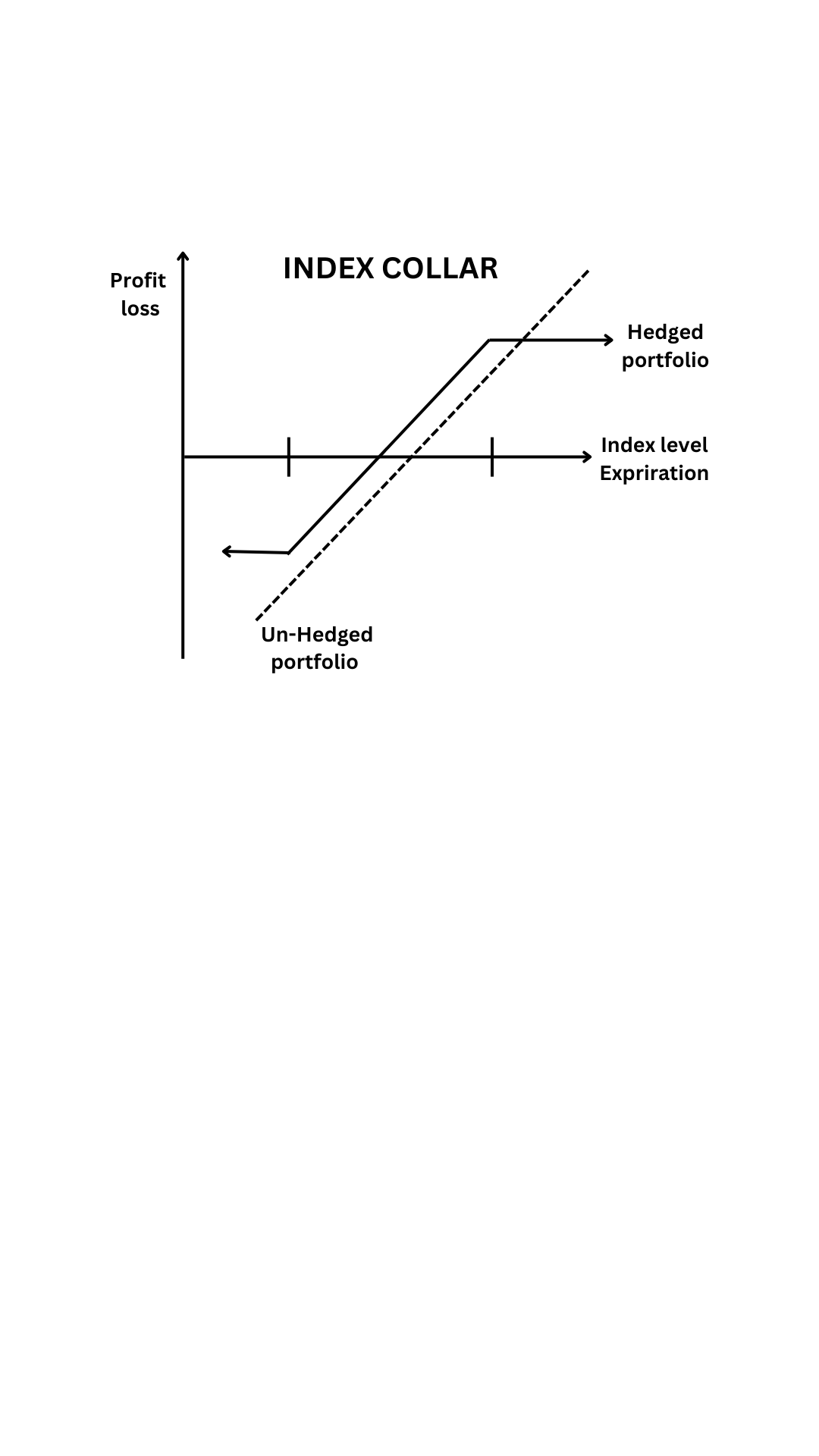
Exchange exposure: Exchange exposure is the degree to which an organization is affected by exchange rate fluctuations. There are three types of exchange exposure: transaction exposure, translation exposure, and economic exposure.
Transaction exposure: This occurs when an organization has a pending transaction denominated in a foreign currency, such as an import or export. Fluctuations in the exchange rate between the transaction date and settlement date can result in gains or losses for the organization.
Translation exposure: This occurs when an organization has foreign assets or liabilities denominated in a foreign currency. Fluctuations in exchange rates can result in gains or losses when these assets or liabilities are translated into the organization’s reporting currency.
Economic exposure: This occurs when an organization’s cash flows and profits are affected by changes in exchange rates. This can happen, for example, when a change in exchange rates affects the competitive position of the organization in international markets.
Exchange risk: Exchange risk is the potential loss that an organization faces as a result of exchange rate fluctuations. Exchange risk can be managed through various strategies, such as hedging, diversification, and risk-sharing arrangements.
Overall, exchange risk is an important consideration for organizations engaged in international trade or investment. Managing exchange risk effectively can help organizations to minimize potential losses and maximize their chances of success in the global marketplace.