Models of Dicision Making
Classical, Administrative Herbert Simon’s Model
Classical management theory, administrative theory, and Herbert Simon’s model are three different approaches to management that have been proposed by different theorists over time. Here is a brief overview of each approach:
Classical management theory: The classical management theory was developed in the late 19th century and early 20th century by theorists such as Henri Fayol and Frederick Taylor. This theory emphasizes the importance of a structured and hierarchical organization, where tasks are standardized, and decisions are made at the top of the organization. The focus is on improving efficiency, productivity, and profitability through careful planning and control.
Administrative theory: The administrative theory, also known as the bureaucratic theory, was developed by Max Weber in the early 20th century. This theory emphasizes the importance of a highly structured organization, where rules, procedures, and policies are carefully defined and followed. The focus is on achieving efficiency and effectiveness through a clear division of labor and a formal hierarchy of authority.
Herbert Simon’s model: Herbert Simon was a management theorist who proposed an alternative approach to management in the mid-20th century. His model emphasizes the importance of decision-making in management and suggests that managers should focus on making rational decisions based on careful analysis and evaluation of all available options. The model proposes that managers should use a four-step process of intelligence, design, choice, and implementation to make effective decisions.
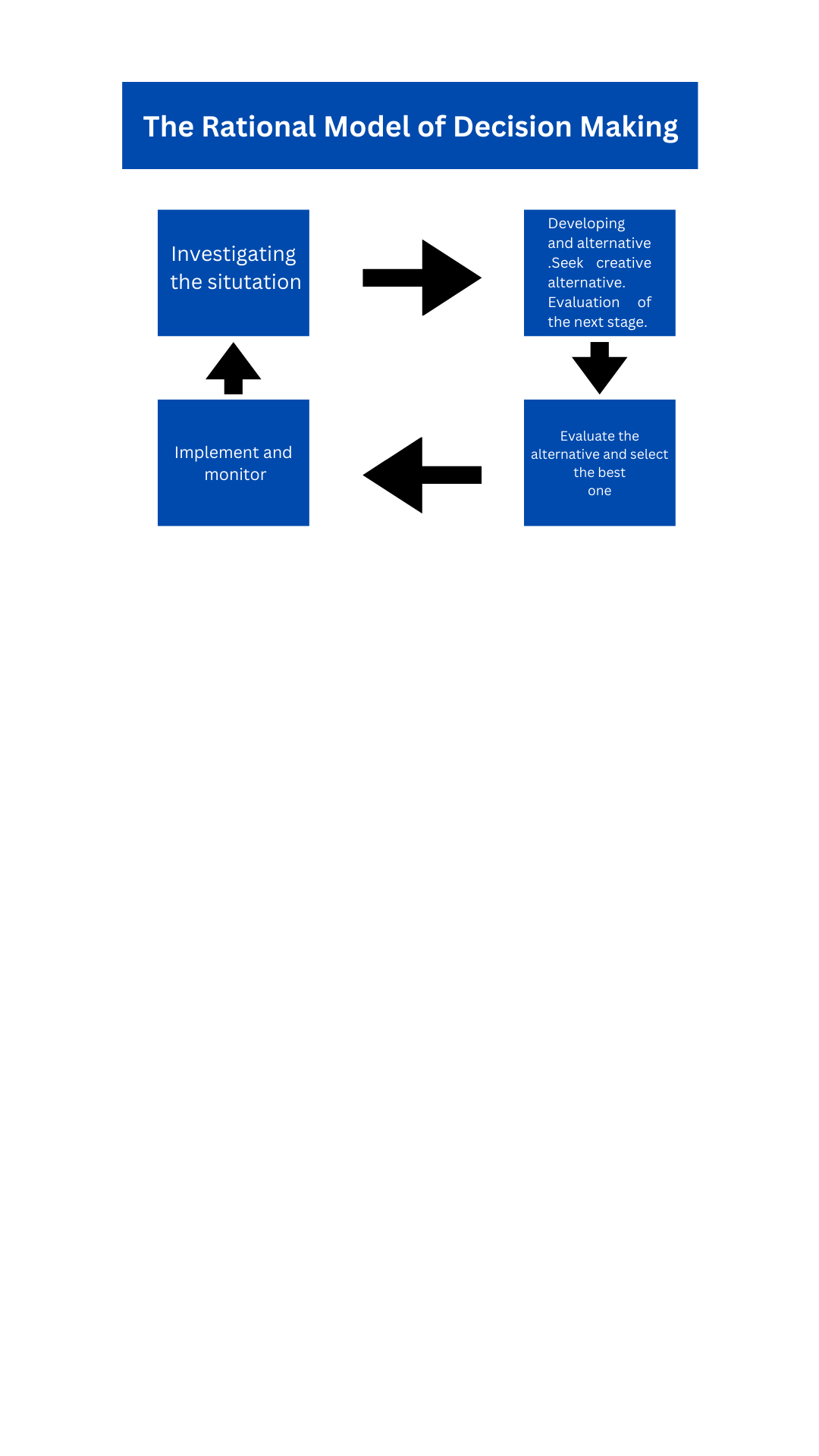
In summary, classical management theory emphasizes efficiency and productivity, administrative theory emphasizes structure and bureaucracy, while Herbert Simon’s model emphasizes decision-making and rational analysis. Each approach has its strengths and weaknesses, and different organizations may find that one approach is more effective than another depending on their specific needs and circumstances.
Management Support System
Management Support Systems (MSS) are computer-based systems that help managers make informed decisions by providing relevant information and analytical tools. These systems are designed to support decision-making at various levels in the organization, from operational to strategic.
MSS typically include the following components:
Data management: MSS collect and store data from various sources, including internal databases, external sources, and user inputs.
Analytical tools: MSS provide a range of analytical tools to help managers analyze and interpret data, including statistical analysis, forecasting, simulation, and optimization.
Decision models: MSS incorporate decision models that help managers evaluate different options and make informed decisions based on the available data.
Reporting and visualization: MSS provide reporting and visualization tools that help managers communicate their findings and insights to others in the organization.